India Implements New GST Rates on Car Purchases
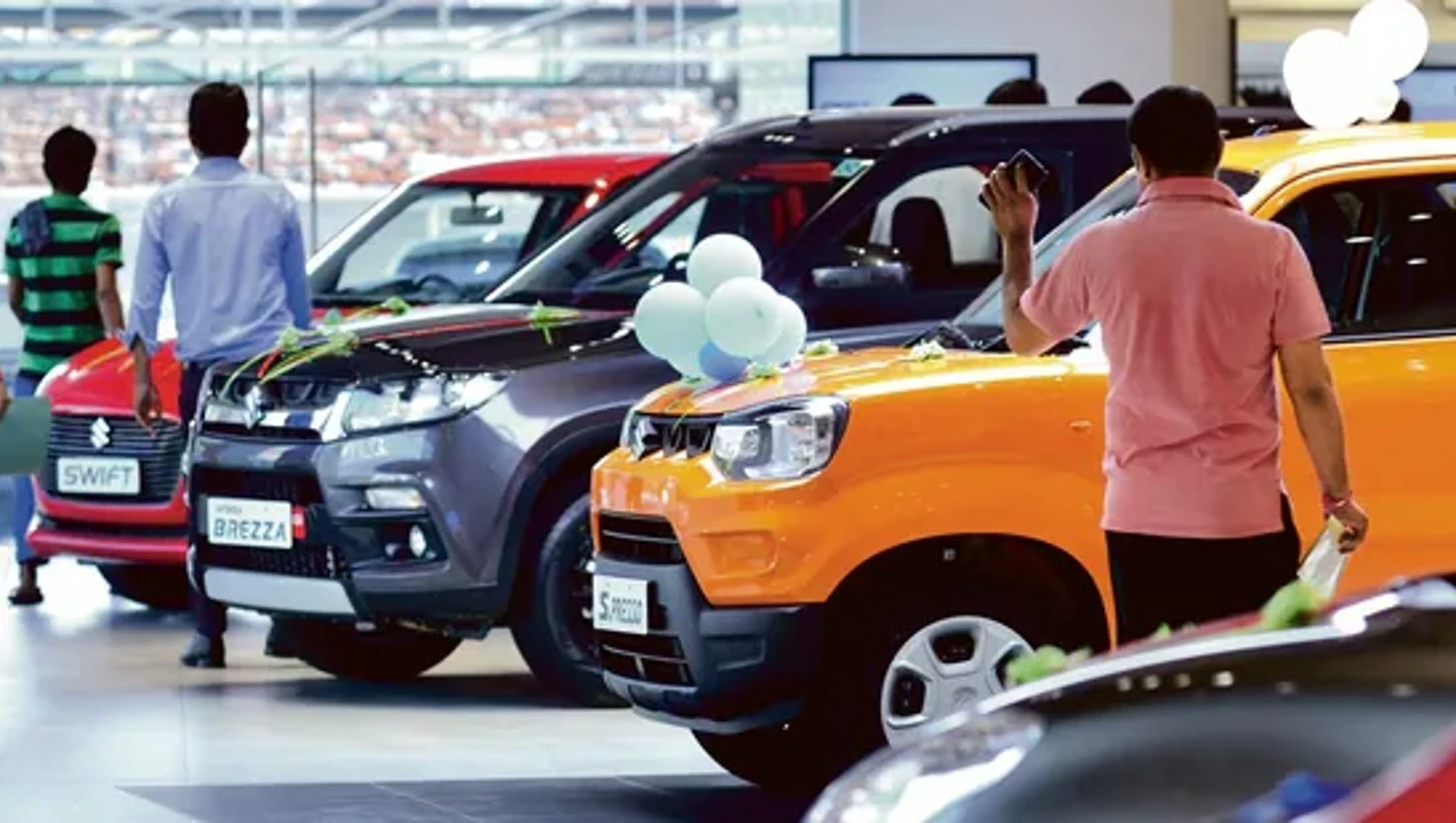

India Implements New GST Rates on Car Purchases
The Indian government has revised GST rates for cars, aiming to boost affordability and enhance personal mobility.
The Indian government has announced revisions to the Goods and Services Tax (GST) applicable to automobiles, a move aimed at enhancing the affordability of both small and large vehicles in the country. This decision follows a long-standing request from the automotive industry for a tax reduction, designed to stimulate the personal mobility sector in India, which ranks as the third-largest car market globally yet sees low vehicle ownership rates of approximately 32 to 34 cars per 1,000 people.
New Tax Structure
As part of the changes, the GST Council has reduced the tax rate on small cars—defined as vehicles with a length of less than four metres and an engine capacity of less than 1,200 cc for petrol and CNG/LPG models—included from 28% to 18%. Additionally, larger vehicles, such as SUVs, will now be taxed at a flat rate of 40%, as the previous additional cess has been removed. Electric vehicles will maintain a lower GST rate of 5%, while all automotive components will also be taxed at 18%.
Saurabh Agarwal, a partner and automotive tax leader at Ernst & Young, expressed optimism regarding the impact of the revised tax rates. He stated, "This decision will not only make vehicles more affordable, but also simplify the classification disputes that have long been a source of ambiguity for the industry. The removal of cess will provide crucial support to a sector that is a vital engine of economic growth."
Broader Access to Personal Mobility
Shailesh Chandra, president of the Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers, highlighted the positive implications of the new rates. He noted that this reform is expected to benefit first-time buyers and middle-income families significantly, offering broader access to personal mobility options.
Looking Ahead
The GST updates will take effect on September 22, 2025. Industry experts anticipate that manufacturers will soon announce revised vehicle prices in line with the new tax structure, marking a shift that is expected to make both entry-level and luxury vehicles more accessible to consumers.
The previous tax rate structure, with total taxes reaching as high as 50% on larger SUVs and luxury cars, is being replaced by a uniform rate of 40%. This change is expected to remove some of the financial barriers that have previously limited access to premium vehicles.
Challenges Ahead
While the revisions are anticipated to enrich the automotive sector, there remain uncertainties regarding whether manufacturers will transfer any cost savings to customers. Additionally, the GST rate on automotive parts has been reduced from 12% to 5%, which could potentially lower production costs, although it remains unclear if this will translate into reduced prices for consumers.
Overall, these GST changes reflect the Indian government's commitment to enhancing the accessibility of vehicles for all citizens, aligning with broader economic objectives aimed at boosting consumer spending and supporting the automotive industry’s recovery in the aftermath of recent challenges, including the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
For prospective car buyers, the forthcoming period could present a unique opportunity to purchase vehicles at more competitive rates, as the government seeks to stimulate economic growth through improved personal mobility solutions.
New Tax Structure
As part of the changes, the GST Council has reduced the tax rate on small cars—defined as vehicles with a length of less than four metres and an engine capacity of less than 1,200 cc for petrol and CNG/LPG models—included from 28% to 18%. Additionally, larger vehicles, such as SUVs, will now be taxed at a flat rate of 40%, as the previous additional cess has been removed. Electric vehicles will maintain a lower GST rate of 5%, while all automotive components will also be taxed at 18%.
Saurabh Agarwal, a partner and automotive tax leader at Ernst & Young, expressed optimism regarding the impact of the revised tax rates. He stated, "This decision will not only make vehicles more affordable, but also simplify the classification disputes that have long been a source of ambiguity for the industry. The removal of cess will provide crucial support to a sector that is a vital engine of economic growth."
Broader Access to Personal Mobility
Shailesh Chandra, president of the Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers, highlighted the positive implications of the new rates. He noted that this reform is expected to benefit first-time buyers and middle-income families significantly, offering broader access to personal mobility options.
Looking Ahead
The GST updates will take effect on September 22, 2025. Industry experts anticipate that manufacturers will soon announce revised vehicle prices in line with the new tax structure, marking a shift that is expected to make both entry-level and luxury vehicles more accessible to consumers.
The previous tax rate structure, with total taxes reaching as high as 50% on larger SUVs and luxury cars, is being replaced by a uniform rate of 40%. This change is expected to remove some of the financial barriers that have previously limited access to premium vehicles.
Challenges Ahead
While the revisions are anticipated to enrich the automotive sector, there remain uncertainties regarding whether manufacturers will transfer any cost savings to customers. Additionally, the GST rate on automotive parts has been reduced from 12% to 5%, which could potentially lower production costs, although it remains unclear if this will translate into reduced prices for consumers.
Overall, these GST changes reflect the Indian government's commitment to enhancing the accessibility of vehicles for all citizens, aligning with broader economic objectives aimed at boosting consumer spending and supporting the automotive industry’s recovery in the aftermath of recent challenges, including the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
For prospective car buyers, the forthcoming period could present a unique opportunity to purchase vehicles at more competitive rates, as the government seeks to stimulate economic growth through improved personal mobility solutions.
Apple's Siri Upgrade Could Use Google Gemini AI by 2026
Apple plans to enhance Siri with Google's Gemini AI, a move aimed at improving voice assistant capabilities by 2026, amid rising competition.
| 2025-09-05
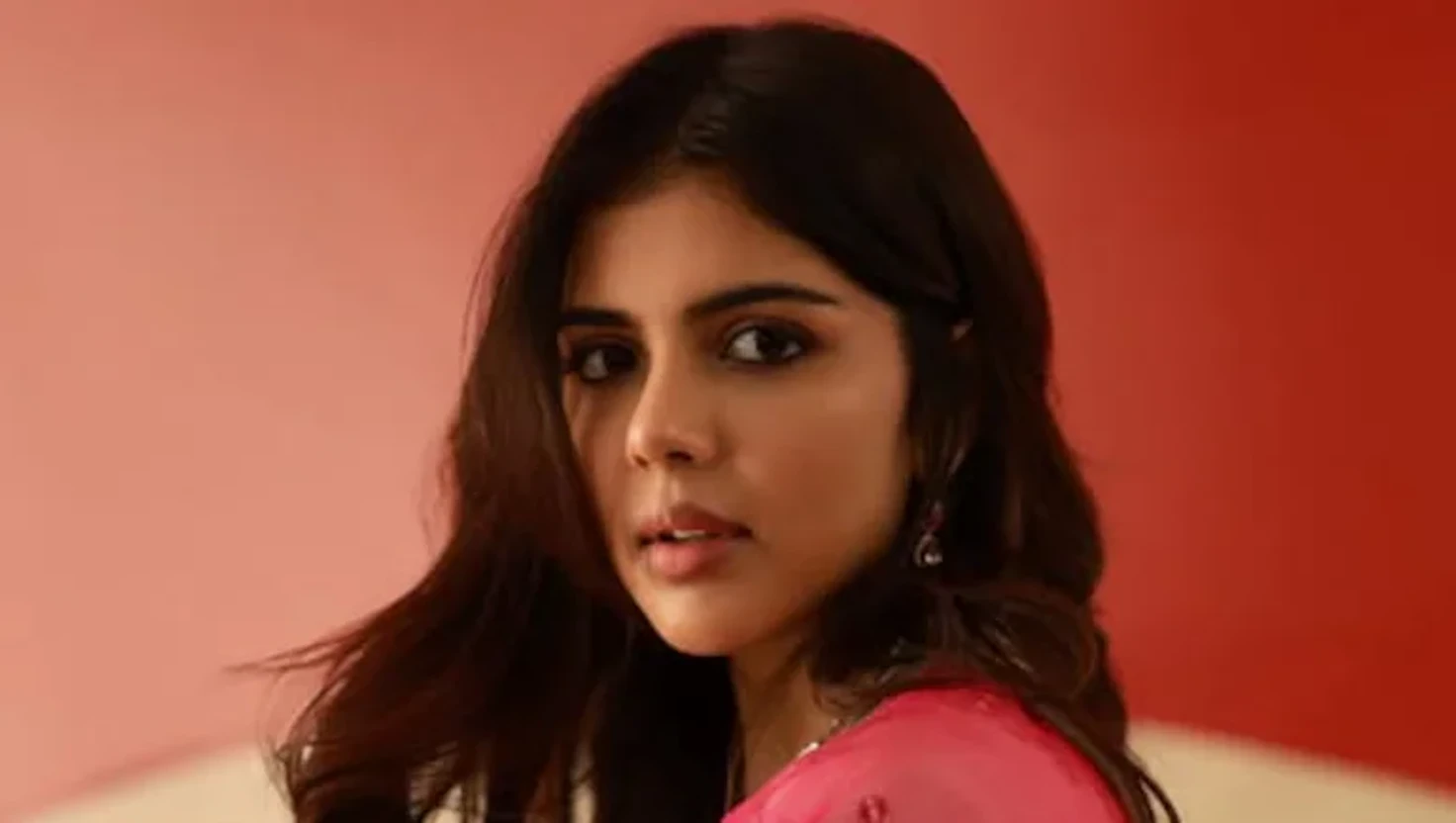

Kalyani Priyadarshan Shines as First Female Superhero in Lokah
Kalyani Priyadarshan's remarkable debut in Lokah Chapter 1: Chandra highlights her family's cinematic legacy and reshapes Malayalam cinema.
| 2025-09-05
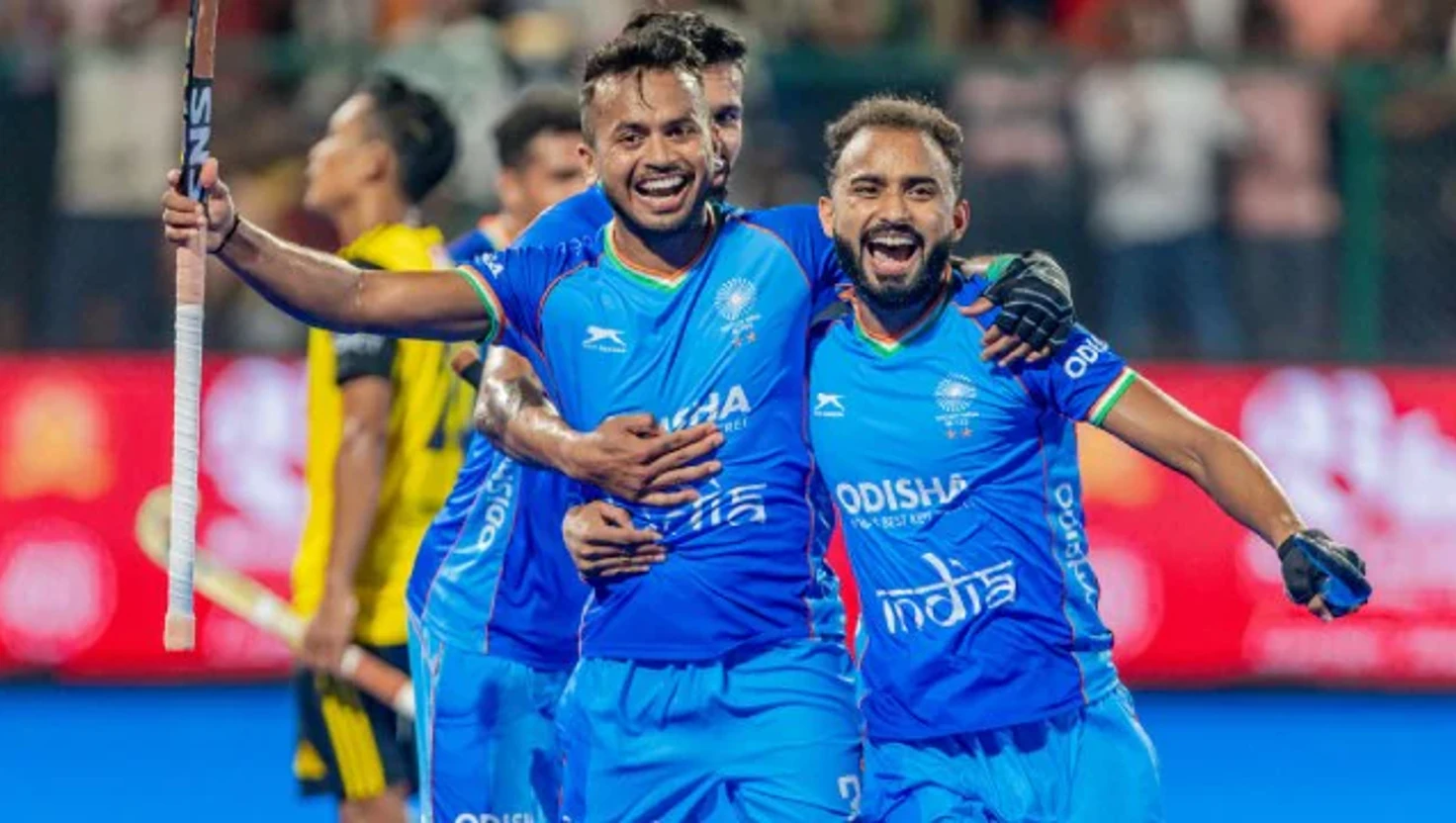

Asia Cup 2025: India Secures Dominant Victory Over Malaysia
India triumphed over Malaysia 4-1 in the Asia Cup Super 4s, boosting their chances for the final. The team displayed resilience despite an early setback.
| 2025-09-05

Trump rules out cut in 50% tariffs on India, hints at additional escalatory measures against Russia
US President Trump reiterates India sanctions as pressure on Moscow, ruling out tariff cuts, amidst strained US-India trade relations.
| 2025-09-04

Trump again slams 'tremendous' Indian tariffs, labels US-India trade 'one-sided'
US President Donald Trump claims India's tariffs on American goods create a one-sided trade relationship, citing Harley-Davidson as an example.
| 2025-09-03




